In the digital age
Both ECOMMERCE and marketplaces have completely changed the way we buy and sell products online. However, although both concepts are related to online sales, there are crucial differences between them. In this article we will explore key differences between ecommerce and marketplaces, and how each of them can be beneficial to buyers and sellers in today’s digital environment.
- What is Ecommerce and what is Marketplace?
Electronic commerce, or ecommerce, relates to the sale of products or services through a business’ own online platform. In ecommerce, a business sets up and manages its own online store, where customers can shop directly from the company.
On the other hand, marketplaces are online platforms that bring together multiple sellers and offer a wide range of products from different brands and suppliers in one place. Marketplaces act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, making transactions easier and providing a common infrastructure for selling. Examples include AMAZON and MERCADOLIBRE.
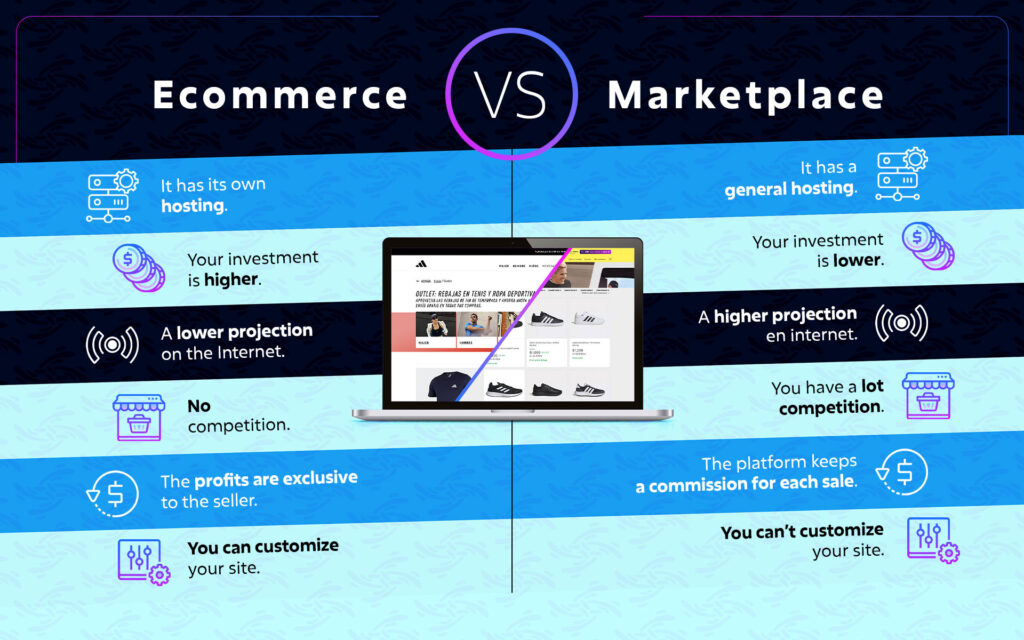
- Ownership and control
In e-commerce, companies have full ownership and control over their online store. They are free to design, customize and manage their platform according to their own needs and requirements. They make decisions about design, product catalog, pricing and marketing strategies.
In marketplaces, ownership and control lie on the platform itself. Sellers enroll into the marketplace and use the infrastructure provided by the platform to sell their products. While sellers may have some level of customization in terms of product listings and pricing, they do not have the same level of control over the platform as they would have in their own online store.
- Audience and outreach
Ecommerce or online stores generally focus on a specific audience or a company’s existing customer base. The company works on driving traffic to its website and attracting customers through their own marketing and promotional strategies.
Marketplaces, on the other hand, already have an established audience and an active customer base. Shoppers visit marketplaces to search and compare products from different sellers in one place. Sellers can take benefit from the reach and visibility offered by the marketplace, as they get wider exposure that can result in a higher volume of sales.
- Logistics and customer service
In e-commerce, the company is responsible for managing logistics, from storage to shipping and customer service. This means that the company must manage its inventory, arrange product delivery, and provide customer support at all stages of the buying process.
In marketplaces, the platform generally handles logistics and provides shipping and customer support services. Marketplaces usually have established systems for managing orders, coordinating shipments and solving purchase-related problems. This frees sellers from the logistics load and allows them to focus more on the production and marketing of their products.
- Costs and commissions
In e-commerce, associated expenses include the setup and maintenance of the online store, marketing fees, paid services, and shipping costs. Sellers take full responsibility for these costs and must manage their own profit margins.
On marketplaces, sellers generally pay commissions or fees to the platform for each completed sale. These commissions may vary from marketplace to marketplace and may affect sellers’ profit margins. However, marketplaces provide an established infrastructure, customer traffic and additional services that may justify these commissions.
Ultimately, both e-commerce and marketplaces offer significant opportunities for businesses and buyers in the digital world. While e-commerce allows companies to have total control over their online presence and brand, marketplaces provide broader access to an established audience and take care of the logistics. The decision between e-commerce and marketplaces depends on the specific goals and needs of each company. So it’s up to you to choose what’s best for your business.


No Comments